The majority of insects develop by complete metamorphosis. Immature stages of these insects look completly different than the adult.
- Mouth parts are tube-like, adapted for sucking and piercing; older nymphs start to develop wing pads, later instars are similar to the adults but smaller

- Small, plump bodied insects with small heads; nymphs and adults of aphids vary in color from yellow to green to nearly black
- Flies undergo a complete metamorphosis. The larvae, however, are commonly referred to as maggots. Most maggots are white and translucent when newly hatched, they have a segmented body, and no legs.
- Coleoptera larvae are usually with legs and have a distinct head capsule, the head is well-developed with ocelli and chewing mouthparts, three pairs of thoracic legs; no abdominal prolegs
 Body form:
Body form:
Campodeiform – Slender, active crawlers
Scarabaeiform — Grub-like, fleshy, c-shaped body
Elateriform — Wireworms; elongate, cylindrical, tiny legs - True bugs undergo simple metamorphosis developing through only three life stages: egg, nymph, and adult. A triangular area, known as the scutellum, is evident on the middle area of the thorax. Nymphs look similar to adults. If wings are present, the front pair is partially thickened or leathery, the second pair membranous
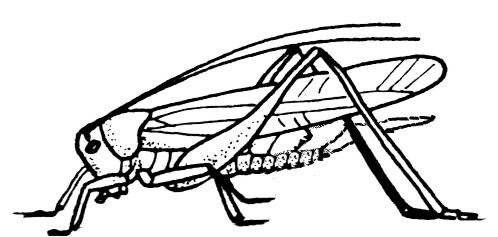
- First pair of wings are leathery and veined throughout, Hind legs generally enlarged and adapted for jumping; Grasshoppers and crickets develop gradually, the young look similar to the adults. All life stages have chewing mouthparts.
- Butterflies and moths undergo complete metamorphosis: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. The larvae, commonly known as caterpillars, have chewing mouthparts.
 Noctuidae (cutworm moths). The Noctuidae is a large including species of economic importance like armyworms, cutworms, bollworms, and loopers. They are primarily foliage feeders, but many species also consume stems and fruits.
Noctuidae (cutworm moths). The Noctuidae is a large including species of economic importance like armyworms, cutworms, bollworms, and loopers. They are primarily foliage feeders, but many species also consume stems and fruits.
Pyralidae (snout and grass moths). The small moths of this family have a prominent snout (labial palps) and are commonly found in grassy areas, like the European corn borer.
Sphingidae (sphinx moths). The larvae of sphinx moths almost always have a spinelike projection on their eighth abdominal segment and, therefore, are commonly known as hornworms. These foliage feeders are a threat to many solanaceous crops. - Metamorphosis in thrips is usually considered simple or gradual, although in some ways resembling complete metamorphosis. The first two wingless instars are known as larvae. During the next one or two instars (depending on the species) as wings become apparent, thrips are called prepupae. A pupal resting stage precedes adult emergence.
